Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Here’s something surprising: according to industry surveys, over 35% of people who meet with a financial professional don’t actually know their official title. Many call them advisors, brokers, or planners, but often, they’re working with a financial representative.
So, what exactly does a financial representative do? In this guide, we’ll unpack their daily responsibilities, career opportunities, and the real value they bring to clients. Whether you’re considering working with one or thinking of becoming one, this article will give you a clear, 360-degree view.
A financial representative is usually the first professional people meet when stepping into the financial services world. Their main role is to connect clients with financial products such as insurance, retirement accounts, or basic investments. They act as a representative of a company, helping clients understand the options available and guiding them through paperwork, applications, and decisions. Think of them as the bridge between a customer and the often-complicated financial system.
This is where a lot of confusion happens. A financial representative isn’t quite the same as a financial advisor or a stockbroker.
In many cases, they work alongside advisors and brokers, but their role is more introductory and relationship-focused.
Financial representatives are employed across a wide range of sectors, but the most common include:
While the setting may differ, the heart of the role remains the same, helping people make sense of their financial choices and pointing them toward the right solutions.
At the heart of the job, a financial representative’s role is to meet clients where they are in their financial journey and guide them toward better decisions. Their responsibilities stretch from the very first conversation with a client all the way through to ongoing support years later.
The first step is always listening. A financial representative spends time learning about a client’s situation, whether they’re saving for retirement, trying to pay off debt, or just opening their first account. These conversations set the tone for everything else, because without understanding goals, it’s impossible to recommend the right solutions.
Once they understand a client’s needs, financial representatives explain products in simple, approachable terms. That might mean walking through the difference between term and whole life insurance, comparing retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s, or showing how mutual funds work. Their job isn’t to overwhelm with jargon, it’s to make financial products less intimidating.
Behind the scenes, there’s plenty of admin work too. Financial representatives often handle applications, contracts, and compliance documents. They guide clients through forms, making sure everything is complete and accurate, which helps avoid costly mistakes down the line.
The relationship doesn’t end once the paperwork is signed. A strong financial representative follows up with clients regularly, checking in on changes in income, family life, or financial priorities. This ongoing support builds trust and ensures clients feel cared for long after the initial meeting.
Finding new clients is a major part of the role, especially early on. Representatives might cold call, host educational seminars, or attend local networking events to meet prospects.
The real skill isn’t just landing a client, it’s keeping them. Building genuine trust is what leads to long-term relationships and repeat business.
Over time, satisfied clients become the best marketing tool. Many seasoned representatives grow their book of business largely through referrals.
Finances can feel overwhelming. A financial representative simplifies the hard stuff so clients actually understand what they’re signing up for.
No two clients are the same. Representatives tailor recommendations to match individual goals, whether that’s saving for a child’s college or planning early retirement.
When clients need advanced planning, the financial representative connects them with advisors, estate planners, or investment managers who can dig deeper.
Being a financial representative isn’t just about knowing products, it’s about connecting with people, earning trust, and staying compliant in a highly regulated industry. To succeed, there are a few skills that make all the difference.

Strong communication skills help representatives put clients at ease and explain complicated concepts in simple terms.
Active listening means going beyond surface-level details to uncover what really matters to a client’s financial life.
Each client is unique, so being able to adapt communication style is essential.
From insurance to mutual funds, a representative needs a strong grasp of the tools they recommend.
Financial services evolve quickly, and ongoing education keeps representatives relevant.
The best representatives translate technical terms into real-world examples clients can actually use.
Financial representatives must operate within strict rules set by organizations like FINRA and state insurance boards.
Ethics play a huge role, recommending products that truly serve the client builds credibility.
Trust is everything, and protecting client information is non-negotiable.
Not every client will say yes, and resilience is key to long-term success.
The goal isn’t to “hard sell” but to match clients with products that genuinely fit their needs.
Strong people skills help expand a representative’s reach through referrals and community connections.
Talking about money is always the interesting part, especially when the career itself revolves around finances. Salary and job outlook for financial representatives in 2025 are shaped by experience, location, and the type of firm they work for.
Most financial representatives in the U.S. earn between $48,000 and $70,000 per year, according to recent industry data. Entry-level roles can start closer to the low end, while seasoned representatives with large client bases may earn well above the average.
Big financial hubs like New York, Chicago, or San Francisco tend to pay more due to cost of living and demand. Smaller markets may offer lower salaries but also come with less competition.
Education, licensing, performance, and company structure all play major roles in determining total earnings.
Some companies offer a steady base salary plus modest bonuses, which creates stability but limits earning potential.
Others rely heavily on commission, meaning pay is tied directly to sales performance. This can be lucrative for high performers but risky for those starting out.
Many firms now use a hybrid system, offering a base salary with the opportunity to earn commission and bonuses. This balance helps new representatives stay afloat while rewarding strong performance.
Representatives can move into senior roles, mentor new hires, or transition into management positions.
With more licenses and experience, many representatives eventually step into financial advisor or planner positions where they handle more complex portfolios.
Some choose to specialize, focusing solely on insurance, retirement planning, or investments. This often leads to higher income and credibility within a niche.
According to projections from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, financial services roles are expected to grow steadily through 2030, with insurance and retirement planning driving demand.
As more people seek professional guidance for retirement and investment decisions, the need for entry-level representatives remains strong.
Digital platforms and AI are changing the way financial services operate, but human representatives remain essential for building trust and handling personalized advice.
Breaking into this career isn’t overly complicated, but it does require education, licensing, and people skills. Here’s the step-by-step path most professionals follow in 2025.
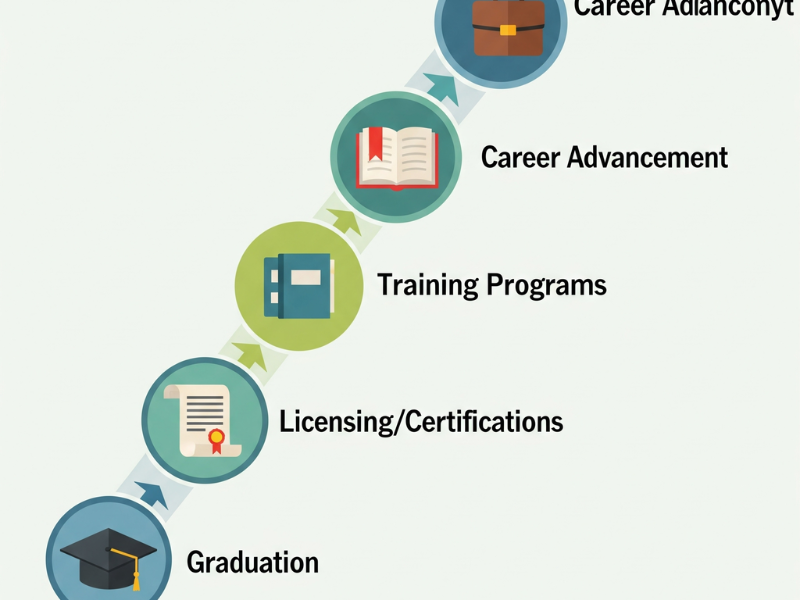
Most firms require at least a bachelor’s degree in finance, business, economics, or a related field. Some may consider strong candidates with other degrees if they demonstrate strong communication and analytical skills.
Courses in accounting, statistics, marketing, and personal finance are especially helpful. Public speaking or communications classes also give an edge since the role is client-facing.
Beyond academics, companies look for strong interpersonal skills, active listening, and the ability to explain financial concepts in plain language.
To sell securities like mutual funds and stocks, financial representatives often need FINRA licenses. The Series 6 license covers packaged investment products, while the Series 7 is broader and more advanced.
If the role involves selling insurance, passing a state-specific licensing exam is a must. Requirements vary depending on where you work.
Most licenses require ongoing education to stay compliant with industry standards and regulations.
Some start as bank tellers, customer service reps, or sales associates before moving into financial representative positions.
Internships offer hands-on exposure and are often stepping stones to full-time offers.
Connecting with seasoned professionals, joining financial associations, and seeking mentorship are powerful ways to break in.
Since much of the role is client acquisition, strong sales ability is crucial.
Representatives must analyze client situations and recommend tailored solutions.
Comfort with CRM systems, financial planning software, and online client portals is becoming more important each year.
Like any career, working as a financial representative has both rewards and drawbacks. Understanding these helps you decide if it’s the right fit for you.
With commissions, bonuses, and performance incentives, top representatives can earn a six-figure income. Success is directly tied to effort and client growth.
The role often leads to higher positions like financial advisor, portfolio manager, or even branch director. Many firms offer clear advancement paths.
Representatives work closely with clients, often guiding them for years. This creates trust, loyalty, and meaningful professional connections.
Many positions allow flexible hours, especially once you build a strong client base. Remote work options are also growing in 2025.
Performance is usually measured by how many products you sell or assets you bring in. This can create stress for those not comfortable in sales-driven environments.
Financial services attract ambitious professionals, which makes standing out challenging. Building a steady client base can take years.
Evenings and weekends may be necessary to accommodate clients’ schedules. Early career reps often work extra hours to build momentum.
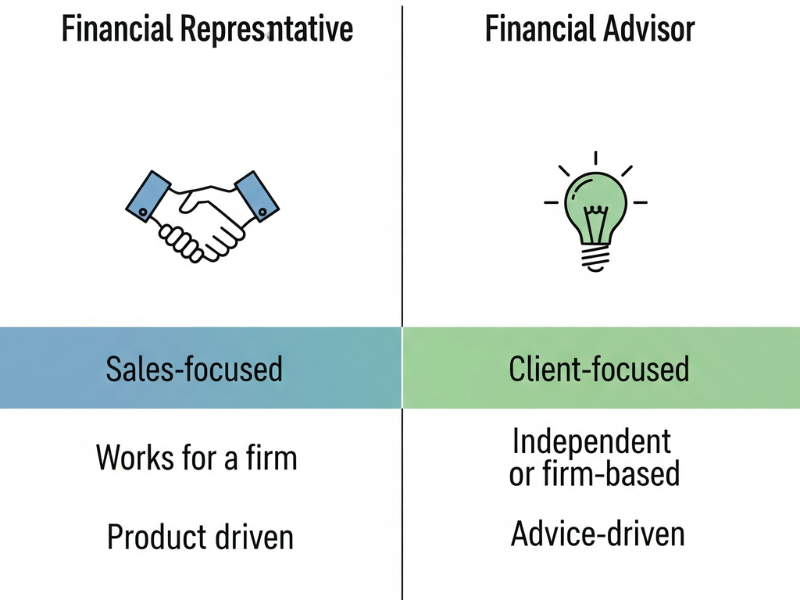
These two titles are often confused, but they’re not identical. Understanding the differences helps clients know who to turn to and helps job seekers choose the right path.
Typically focuses on selling financial products like insurance policies, investment accounts, or retirement plans.
Provides broader financial planning, including investment management, estate planning, and tax strategies.
Usually needs state insurance licenses and possibly securities licenses (like Series 6 or 7).
Often holds advanced certifications such as CFP (Certified Financial Planner) or CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst).
Engages clients mainly for product-specific needs and maintains relationships through regular check-ins.
Takes a long-term, holistic approach, guiding clients through multiple stages of wealth-building.
Earnings are often commission-based, tied to product sales.
May charge fees, earn commissions, or use a hybrid model depending on their firm.
If you only remember one thing, remember this: a financial representative is the on-ramp to real financial planning. They help you translate goals into action, explain products in plain English, and connect you with the right specialists when things get complex. Simple, practical, human.
Use that first meeting to get clarity. Ask about licenses, compensation, and the exact problems they help solve. Bring your numbers, income, debts, insurance, retirement accounts, so the conversation is specific. If a recommendation is not clear, pause and ask for a one-sentence summary. No guesswork, no surprises.
Choosing a financial representative versus a financial advisor comes down to scope. If you are starting out, opening accounts, comparing insurance, or setting up your first retirement plan, a financial representative is a smart move. If you need a full plan, tax-aware investing, or ongoing portfolio management, step up to an advisor. Many people use both at different stages, which is totally fine.
Next steps, pick one action and do it today. Schedule a discovery call, gather your statements, or set a simple savings target you can hit this month. Momentum beats perfection. If the first conversation feels pushy or confusing, walk away and try another pro. Your money deserves fit and trust.
Want more help while you decide? Dive into these guides on your site for quick wins and deeper learning:
Want to dive deeper into financial topics? Check out our other guides: